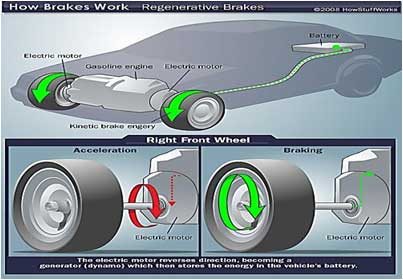
POWER FROM BRAKES
In regenerative braking system, the motor; which drives an electric vehicle, also performs the function of braking. The system consists of an electric motor with dual function. In one direction, it works as a motor, and in the opposite as a generator. When it runs as a motor, it converts electrical energy into mechanical energy and drives the wheels. While braking, it runs in the opposite direction and becomes an electric generator. The system captures and converts this waste energy into electricity. The electricity, thus regenerated; charges the battery of an electric or hybrid vehicle.
- In a battery-powered electric vehicle, regenerative braking is the conversion of the vehicle’s kinetic energy into chemical energy stored in the battery, where it can be used later to drive the vehicle. It is braking because it also serves to slow the vehicle. It is regenerative because the energy is recaptured in the battery where it can be used again.
- The kinetic energy stored in a moving vehicle is related to the mass and speed of the vehicle by the equation E = ½mv². All else being equal, if a car is twice as heavy it has twice the kinetic energy and if it is moving twice as fast it has four times the kinetic energy. Any time a car slows down the kinetic energy stored in the vehicle has to go somewhere.
- There is always some kinetic energy consumed by the rolling resistance, mechanical friction, and aerodynamics of your car. These bits of energy go into heating the road, the surrounding air, and various spinning parts in your car. But the vast majority of the kinetic energy is converted into heat by brake pads when you stomp on the brakes.
- In the Tesla Roadster, regenerative braking recovers some energy that would otherwise have been wasted in the brakes.